GeoLifeCLEF-LifeCLEF-CVPR-FGVC
Species Composition Prediction with High Spatial Resolution at Continental Scale Using Remote Sensing
Overview
The Species Composition Prediction project aims to predict plant species in a given location and time using various predictors such as satellite images, climatic time series, and other rasterized environmental data. This project leverages a large-scale training set of plant occurrences in Europe to develop and validate predictive models.
Project Goals
- Predict Plant Species: Utilize satellite images, climatic time series, land cover, human footprint, bioclimatic, and soil variables to predict plant species at specific locations and times.
- Large-Scale Training and Validation: Provide a substantial training set with millions of plant occurrences and detailed validation and test sets to ensure robust model performance.
- Tackle Challenges: Address multi-label learning from single positive labels, strong class imbalance, multi-modal learning, and large-scale data processing.
Aim to develop and evaluate models that predict plant species
composition at high spatial resolution (∼10m) from diverse type of input environmental predictors,
by calibrating them on two types of species observations: Opportunistic presence-only records and
standardized presence-absence surveys
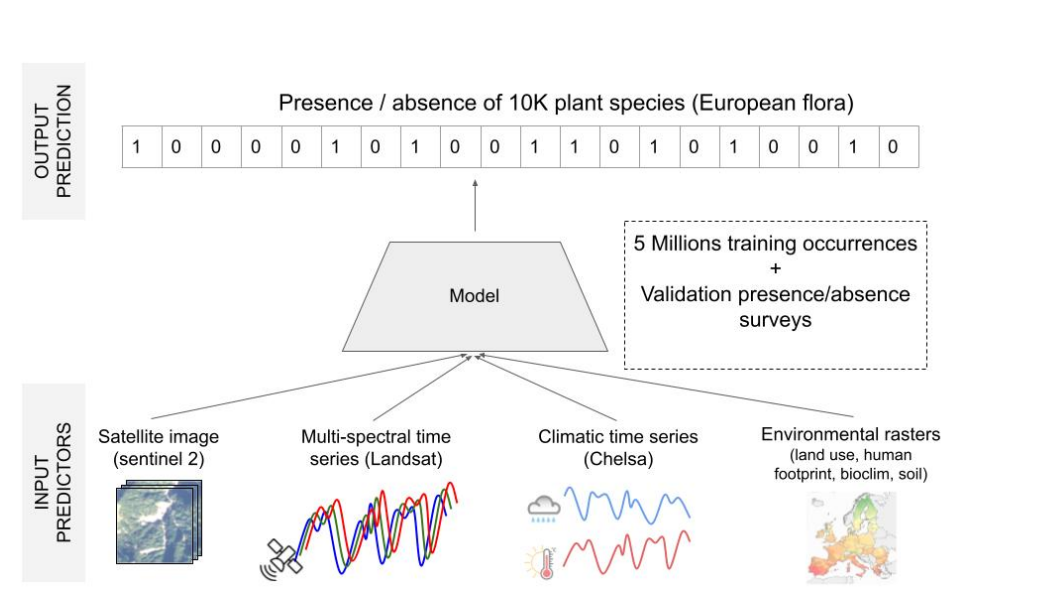 image courtesy : Christophe Botella, Benjamin Deneu, Diego Marcos, Maximilien Servajean, Joaquim Estopinan, et al.. The GeoLifeCLEF 2023 Dataset to evaluate plant species distribution models at high spatial resolution across Europe. 2023. ⟨hal-04152362⟩
image courtesy : Christophe Botella, Benjamin Deneu, Diego Marcos, Maximilien Servajean, Joaquim Estopinan, et al.. The GeoLifeCLEF 2023 Dataset to evaluate plant species distribution models at high spatial resolution across Europe. 2023. ⟨hal-04152362⟩
Dataset
Training Set
- Size: Approximately 5 million plant occurrences
- Type: Single-label, presence-only data
- Region: Europe
Validation Set
- Size: About 5,000 plots
- Type: Multi-label, presence-absence data
Test Set
- Size: 20,000 plots
- Type: Multi-label, presence-absence data
Predictors
The prediction models will use the following types of data:
- Satellite Images and Time Series
- Climatic Time Series
- Land Cover Data
- Human Footprint Data
- Bioclimatic Variables
- Soil Variables
Challenges
- Multi-Label Learning from Single Positive Labels: Handling the complexity of predicting multiple species from data that often contains only a single positive instance.
- Strong Class Imbalance: Managing the disproportionate representation of different species in the dataset.
- Multi-Modal Learning: Integrating diverse types of data (e.g., satellite images and climatic series) effectively.
- Large-Scale Data Processing: Efficiently processing and analyzing a vast amount of data to generate accurate predictions.
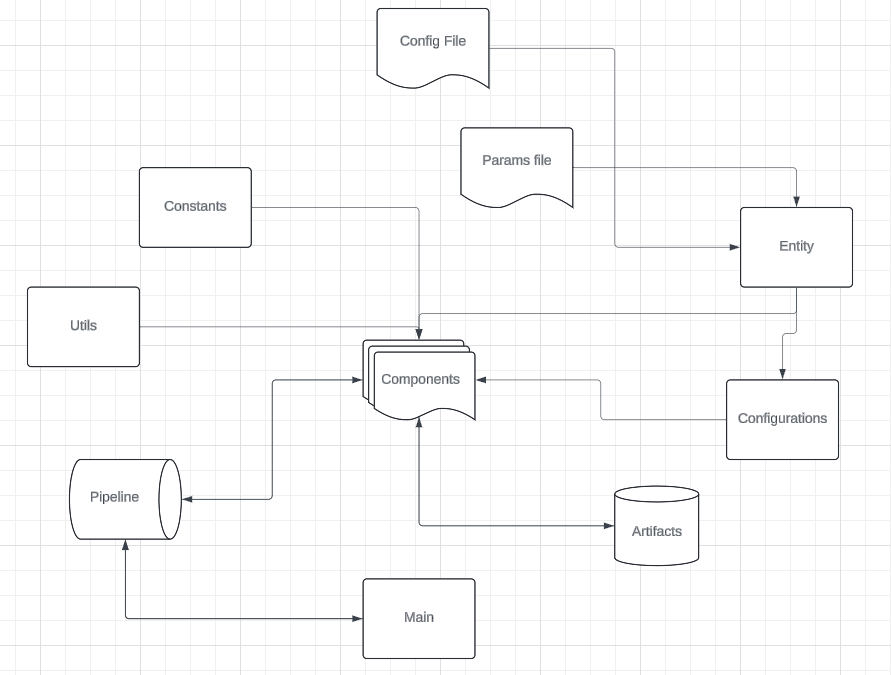
Workflows
Usage
Installation
To get started with the project, clone the repository and install the required dependencies using requirements.txt
Author
Collaborations and contributions are open for this project.
Contact :[yashraj3376@gmail.com]
Read more here:
GeoLifeCLEF-LifeCLEF-CVPR-FGVC Research Repository
References
@misc{geolifeclef-2023-lifeclef-2023-x-fgvc10, author = {Alexis Joly, Benjamin Deneu, César Leblanc, ChrisBotella, Diego Marcos, Maximilien Servajean, tlarcher}, title = {GeoLifeCLEF 2023 - LifeCLEF 2023 x FGVC10}, publisher = {Kaggle}, year = {2023}, url = {https://kaggle.com/competitions/geolifeclef-2023-lifeclef-2023-x-fgvc10} }